Nikola Tesla Patents
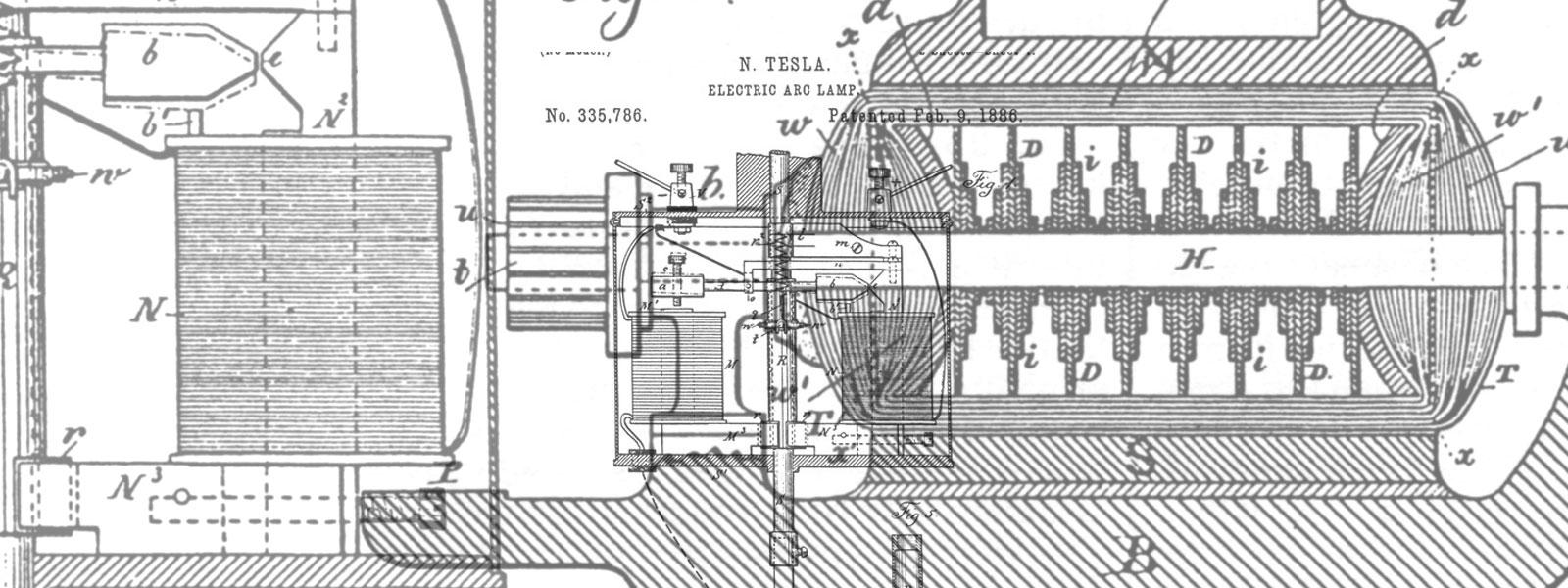
242 The outer circle of contacts comprises two long plates, 7 and 8, on opposite sides of the disk, and a series of shorter plates, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 in the front and rear. Flexible conductors 1', 1" connect the plates and 8 with the terminals of the propelling motor D, . and the poles of the main battery E are connected to the brushes 5 and 6 respectively, so that, while the rudder is. straight or turned up to a certain angle to either side, the current is conveyed through the brushes 5 and 6 and segments 7 and to the propelling motor D. The steering motor F is also driven by current taken from the main battery E in the following manner.. A conductor 15 from one pole of the battery leads to one of the commutator brushes, and from the other brush runs a conductor 16, to one of the contacts of each relay K' K". When one of these relays as K" is active, it continues this circuit through a wire 19, through one field coil or set of coils on the motor P, and thence to the brush 1. In a similar manner, when the other relay K' is active, the circuit is continued from wire 18 through a wire 20, the second or reversing set of field coils and to brush 2. Both brushes 1 and 2, at all times when the rudder is not turned more than about forty-five degrees to one. side, are in contact with a long conducting plate 21, and one brush in any position of the rudder is always in contact with said plate, and the latter is connected by a flexible conductor 22 with the opposite pole of the main battery. Hence the motor F may always be caused to rotate in one direction, whatever may be the position of the rudder, and may be caused to rotate in either direction when(18)
