Nikola Tesla Books
Colorado Springs
Aug. 27, 1899
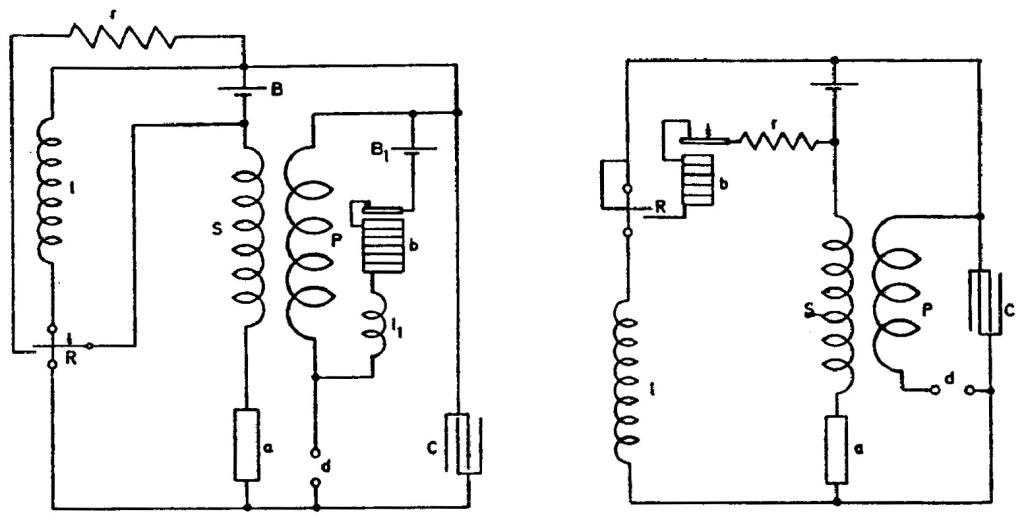
Older plans experimented with and modified arrangements of apparatus for wireless telegraphy further considered.
These connections used to relieve the sensitive device from the strain of the battery after excitation. The necessity of doing this leads to the reconsideration of an old plan experimented with in New York which consists of placing the sensitive device between
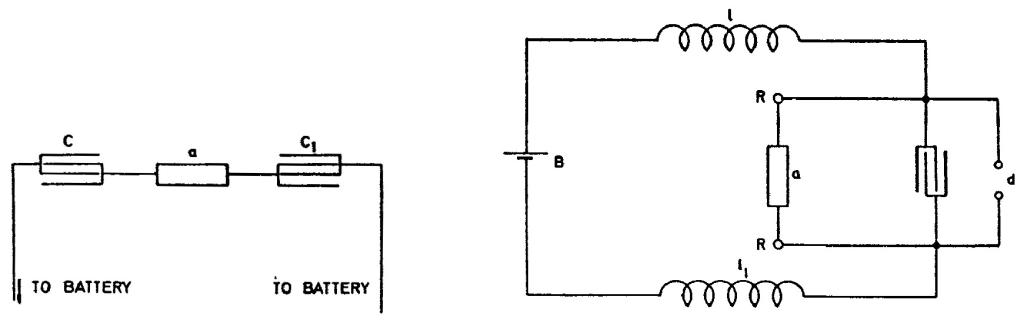
condensers in circuit so that each time only one current impulse can pass through the device. This is illustrated in a general way in the little diagram below. The battery strains the device a through the condensers C C1 but when, upon the device a becoming excited, the condensers are suddenly charged the current impulse caused by the charging automatically stops. It is then necessary to reverse the mains, or discharge the condensers to make the apparatus ready for a second operation. This plan allows use of very high pressure on the sensitive device which should be of great resistance.
Plan in last diagram illustrated consists of raising, by means of inductances l l1, condenser C and break device d, the e.m.f. of battery B so far as needed to bring the device a to the point of nearly breaking down. The quantities should for a better result be adjusted as usual. Both relay coils R R and inductances l l1 are placed symmetrically.
164
August 27
Although he has noted several times already that good results were obtained with various decoherence techniques (rotation, interruption of the excitation current), this re-examination of his old ideas shows that Tesla is still seeking a more reliable solution. One of the ideas he was gathering together for further investigation is illustrated by the diagram in Fig. 4, in which a rotary interrupter, condenser, choke and battery provide bias for the sensitive device. When interrupter d breaks, the voltage on C can be higher than the battery voltage. With proper choice of the values the coherer can be biased to threshold, making it very sensitive.
August 27
He returns to the questions of how to deactivate the receiver's sensitive device. Although he said many times that he achieved good results with various deactivization techniques (rotation, excitation current interruption), he again considers the old ideas which indicates that Tesla still looks for a good solution. Compiling the ideas for further thinking, he shows the scheme on Fig. 4, in which the pre-excitation of the sensitive device is achieved by means of rotating breaker, capacitor, inductive coil and battery. The potential on C, when breaker D is open, could be even higher than the battery voltage. With well adjusted elements desired pre-excitation could be achieved up to "near flash-over" and therefore a very good sensitive device could be obtained.